
Children’s Problems
Children can suffer from the same problems as adults such as ingrown toenails, warts. However the most common problem children suffer from heel /arch pain (Calcaneal apophysitis or Kohler’s disease) as well as knee (Osgood Schlatter), and shin pain (Shin splints) is as result of flat feet.
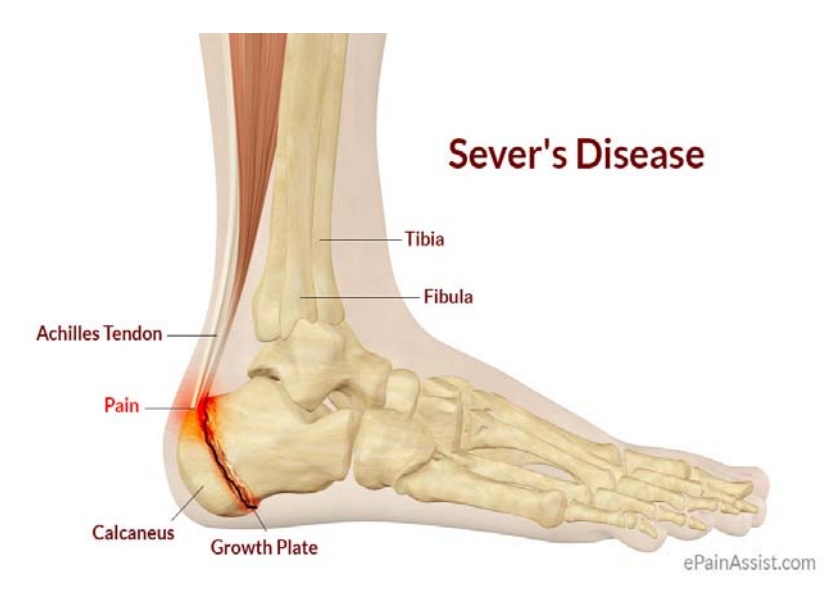 Calcaneal apophysitis also known as Severs disease is an inflammation of the growth plate in the heel of growing children, typically adolescents. The condition presents as pain in the heel and is caused by repetitive stress to the heel and is thus particularly common in active children. It usually resolves once the bone has completed growth or activity is lessened.
Calcaneal apophysitis also known as Severs disease is an inflammation of the growth plate in the heel of growing children, typically adolescents. The condition presents as pain in the heel and is caused by repetitive stress to the heel and is thus particularly common in active children. It usually resolves once the bone has completed growth or activity is lessened.
Treatment may include physical therapy, elevating the heel, stretching hamstrings and calf muscles, rest, ice, anti-inflammatories and or custom foot orthotics.
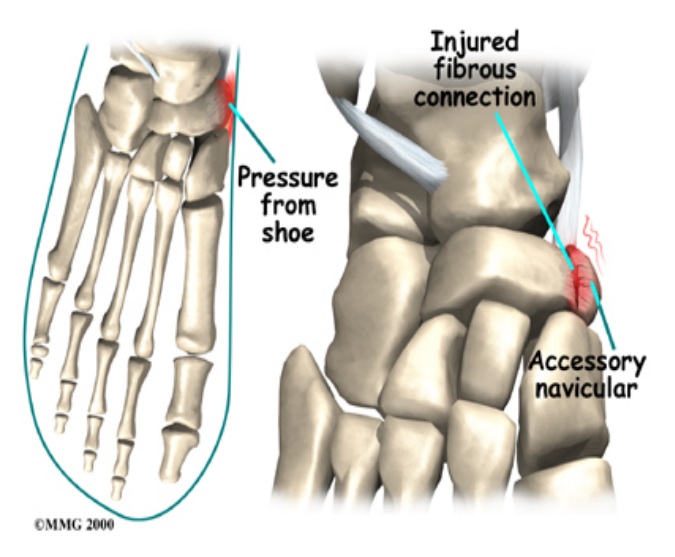 Kohler’s disease is a bone disorder (navicular bone) of the foot in children that may be the result of stress related compression at a critical time during the period of growth.
Kohler’s disease is a bone disorder (navicular bone) of the foot in children that may be the result of stress related compression at a critical time during the period of growth.
Treatment may include resting the affected foot, taking pain relievers and trying to avoid putting pressure on the foot. In acute cases, the patient is often fitted with a below the knee cast. The cast is usually worn for 6 to 8 weeks. Physical therapy may be of some benefit, along with custom fitted foot orthotics.
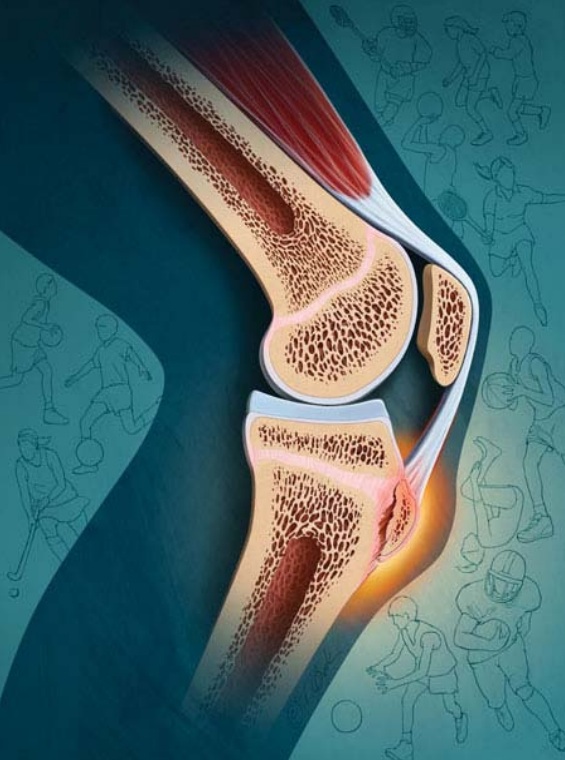 Osgood Schlatter disease also known as an apohysitis of tibial tubercle is an inflammation of the patellar ligament at the tibial tuberosity. It is characterized by a painful lump just below the knee and is most often seen in young adolescents. Risk factors include overuse (especially in sports involving running, jumping and quick changes of direction) and adolescent growth spurts.
Osgood Schlatter disease also known as an apohysitis of tibial tubercle is an inflammation of the patellar ligament at the tibial tuberosity. It is characterized by a painful lump just below the knee and is most often seen in young adolescents. Risk factors include overuse (especially in sports involving running, jumping and quick changes of direction) and adolescent growth spurts.
Treatment may include rest, ice, and specific exercises being recommended, anti-inflammatory medication as well as physical therapy. Custom foot orthotics may be recommended to offset biomechanical abnormalities. Typically symptoms resolve as the growth plate closes.
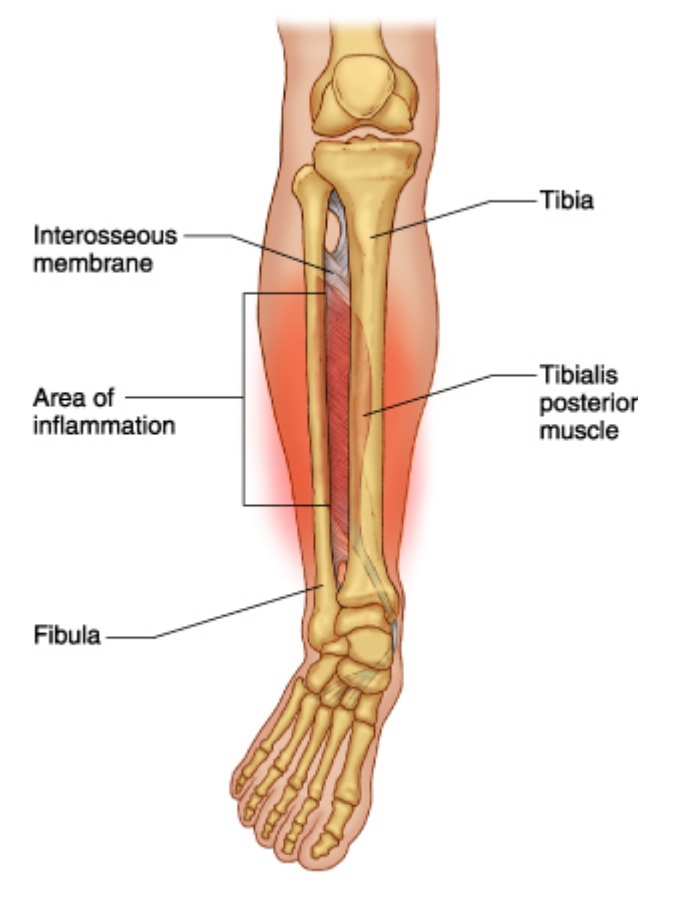 Shin Splints are a pain along the inner edge of the shin bone. Shin splints are usually caused by repeated trauma to the connected muscle tissue surrounding the tibia. They are a common injury affecting athletes who engage in running sports or other forms of physical activity, including running and jumping.
Shin Splints are a pain along the inner edge of the shin bone. Shin splints are usually caused by repeated trauma to the connected muscle tissue surrounding the tibia. They are a common injury affecting athletes who engage in running sports or other forms of physical activity, including running and jumping.
Treatments may include rest, ice, strengthen, anti-inflammatory medication and gradually returning to activity. Custom foot orthotics may be recommended to offset biomechanical abnormalities.




